SICPA: COVID-19 Secured Immunity Passport
04.20.20
A COVID-19 immunity passport secured by blockchain to enable deconfinement
As the coronavirus crisis continues to wreak havoc on the lives of citizens and the economies of more than 190 countries, one of the challenges for governments and local authorities is to manage deconfinement effectively and the progressive return to normal life, as well as preventing further waves of infection.
Several different technological solutions are envisaged, notably movement documents and traceability apps, but all are vulnerable to fraud and falsification and may impact on basic liberties, be discriminatory or be socially unacceptable.
The introduction of an immunity passport or other highly secured health document would help manage the health status of the population in real-time, respecting ethical standards and protecting personal data whilst guaranteeing the issuance, use and verification of certified data that is secured and anonymized.
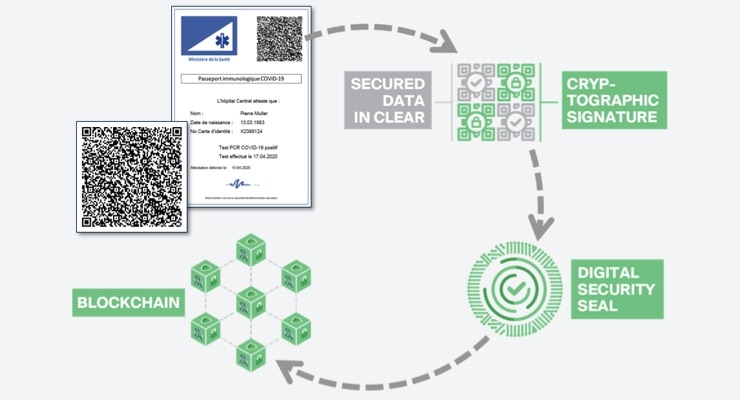
It is against this background that three companies have partnered to propose the “COVID-19 secured immunity passport,” a health passport which will contribute to allowing rapid and safe deconfinement: OpenHealth, a French leader in managing health data for official health authorities and stakeholders in industry, research and the public at large; the Swiss SICPA Group, a global leader in providing authentication and secured traceability technologies; Guardtime, supplier of the KSI Blockchain, the first to be certified according to the European eIDAS standard.
The proposed solution aims to issue and manage immunity passports (“COVID-19 immunity passport”) which would serve as the basis for real-time monitoring of the population’s state of immunity. The KSI Blockchain will make it impossible to falsify and the immunity data on these certificates will be used by the OpenHealth platform to follow the evolution of deconfinement and management of the crisis, following the model of flu pandemics.
SICPA’s Certus technology, provided to the French government in the framework of a trial launched by the Defense Ministry to combat COVID-19, aims to allow all consenting persons who have had an approved test to detect the virus or antibodies, to receive a certificate from an authorized body showing the result of the test, in a digital, but printable, format which cannot be falsified and is universally verifiable.
A simple smartphone app or a computer is all that is required for the verification, including in offline mode, with all personal data about the person tested being anonymized.
The tool is interoperable and works without a central database.
Furthermore, the passport can be updated in real-time (creation, expiration, renewal, cancellation) according to medical test results. The rules for use being defined by the appropriate competent authorities.
In addition to enabling social and economic activity to restart in accordance with the conditions determined by the state, this technology could also allow public authorities to control access to critical or sensitive facilities, such as hospitals and retirement homes, schools, government offices, companies and businesses, taking account of the remaining uncertainties about the virus, evolving health policies and the reliability of tests.
The solution once implemented can support health authorities to measure the efficiency of the deconfinement plan and to monitor in real-time the progressive acquisition of mass immunity.
Looking beyond the crisis, the immunity passport secured by blockchain can help better prepare for the future and serve as a tool to manage any new wave or seasonal reoccurrence of the epidemic. It could also be the cornerstone of a future secured digital vaccination record.
The “COVID-19 secured immunity passport” is designed to meet the highest level of protection of personal data, in accordance with the GDPR, thus assuring both the protection of populations and the respect of the right to privacy.